Energy Savers – the Efficiency and Comfort Experts
The reasons to insulate are many and understanding how insulation works can help you see its true value. From the moment Energy Savers insulates your home or business, the energy savings and increased comfort begin.
An Introduction to Insulation
Although everyone agrees that insulation is an important element of any building, most people aren’t clear on how it works to improve interior comfort and reduce heating and cooling costs nor are they aware of the multiple places energy is lost in a building. As an Owens Corning® Certified Energy Expert® we understand the science behind the building envelope and can suggest the best solution to address your insulation needs.
Why Insulate?
Insulation is an important piece of the energy efficiency puzzle for residential, commercial and industrial structures. It is one of the most cost-effective ways to improve interior comfort and reduce monthly heating and cooling bills. Insulation is also an excellent noise absorber and helps to reduce sound transmission from both outside and within a structure, creating a quieter space with less reverberation.
Whether you are remodeling a home or building a new business space, well-installed insulation offers a host of short-term and long-term advantages:
- Increased, more consistent interior comfort all year long
- Reduced energy usage
- Lower heating and cooling costs
- Less wear and tear on HVAC equipment
- Reduced noise transmission for a quieter space
- Improved air quality for better health
- Reduced moisture intrusion
- Less overall environmental impact

SCHEDULE A CONSULTATION!
Call us today at 502-817-8400 or fill out the form for a free estimate and learn how we can help you save energy.
How Insulation Works
Warm air naturally flows from higher temperature areas to lower temperature areas, creating temperature fluctuation within a space. That means that in the cold winter months the heated air in your home or commercial building tries to escape to the outdoors, while in the warm summer months, the hot air outside tries to force its way in to your nicely conditioned space. Insulation wraps your home in a protective blanket, reducing heat flow in order to keep the heat out during warmer months and the heat in during cooler months.
Insulation alone may not always solve your interior comfort concerns. Quite often it is necessary to seal areas where air can infiltrate the building with caulk or other air sealing materials, forming a comprehensive system that helps maintain consistent temperatures and moisture levels, keeps out allergens, reduces energy usage and decreases monthly heating and cooling bills.
What Is R-Value?
The performance of insulation is typically measured by a common standard known as R-value. The “R” in R-value stands for resistance to heat flow. The higher the R-value, the higher the level of resistance and the greater the insulating power. R-value requirements vary depending on climate and building type as well as local energy codes, which establish the minimum level of insulation needed to create an effective thermal enclosure.
How Much Insulation Is Enough?
The amount of insulation needed varies depending on location, building type and materials. ENERGY STAR, a U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) program that promotes superior energy efficiency, provides recommended and cost-effective insulation levels for homes across the country based on climate zones and are specified by R-Value. R-Value measures the ability of insulation to resist heat traveling through it, with a higher R-Value indicating better thermal performance. A properly insulated home is a comfortable, efficient home.
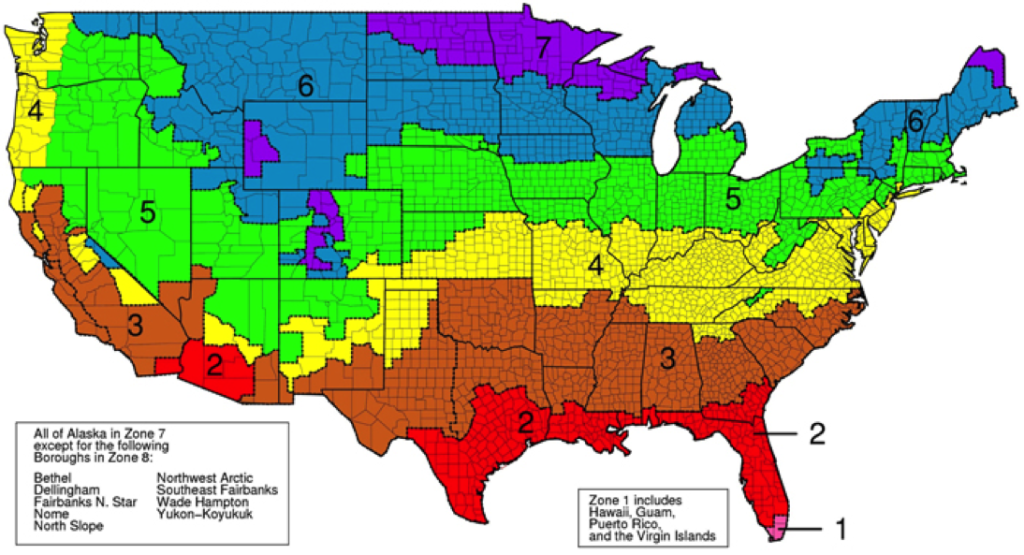
The image below shows the different climate zones and the recommended insulation levels for retrofitting existing wood-framed buildings. According to the North American Insulation Manufacturers Association (NAIMA), more than 90% of homes in the U.S. are under-insulated*. Energy Savers has well over a decade of expertise working in Kentucky and Southern Indiana and we have a broad knowledge of the current code requirements. We will be happy to suggest custom-tailored solutions for your needs that will meet or exceed these requirements and help make sure your home isn’t part of that 90%!
Things to Consider When Insulating
- What type of insulation is being used?
- Does the insulation meet or exceed local building codes and national recommended insulation levels?
- How effective is the insulation for thermal and acoustical performance?
- Is the insulation resistant to moisture, insect and rodent infestation and settling?
- Is the insulation material safe and environmentally friendly?
- Is the insulation cost effective?
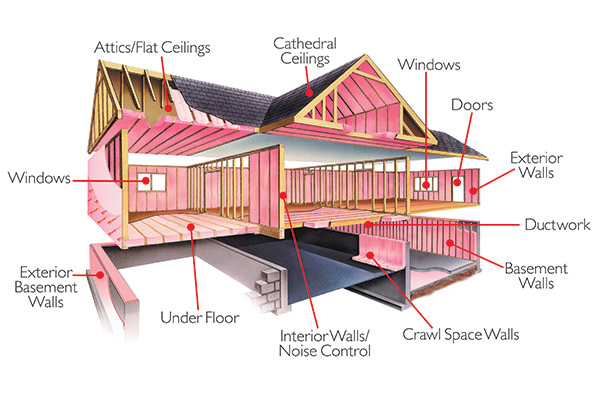
Where to Insulate?
In residential structures, insulation should be installed in walls, floors, attics, basements and crawlspaces. A more detailed list includes:
- Ceilings with unheated spaces above, including dormer ceilings
- Knee walls of attic spaces finished as living areas
- Sloped walls and ceilings of attics finished as living areas
- Cathedral or vaulted ceilings
- Around perimeters of slabs
- Floors above vented crawl spaces
- Floors over unheated or open spaces such as over garages or porches
- Basement walls
- Band and header joists
- Interior walls, ceilings or floors where extra sound control is desired
- Floors over unconditioned basements
